DFA PROJECTS AND USE CASES
DFA Projects and Use Cases are the results of the MUSAE art-tech residencies, exploring innovative intersections between art, technology, and societal challenges. These projects serve as best practices in the Food as Medicine domain, demonstrating the potential of the DFA method and the MUSAE Factory Model. DFA projects are divided into two categories
- Future Scenarios, developed during the first art-tech residency, present visionary scenarios that anticipate emerging trends and opportunities in different areas of the Food as Medicine topic.
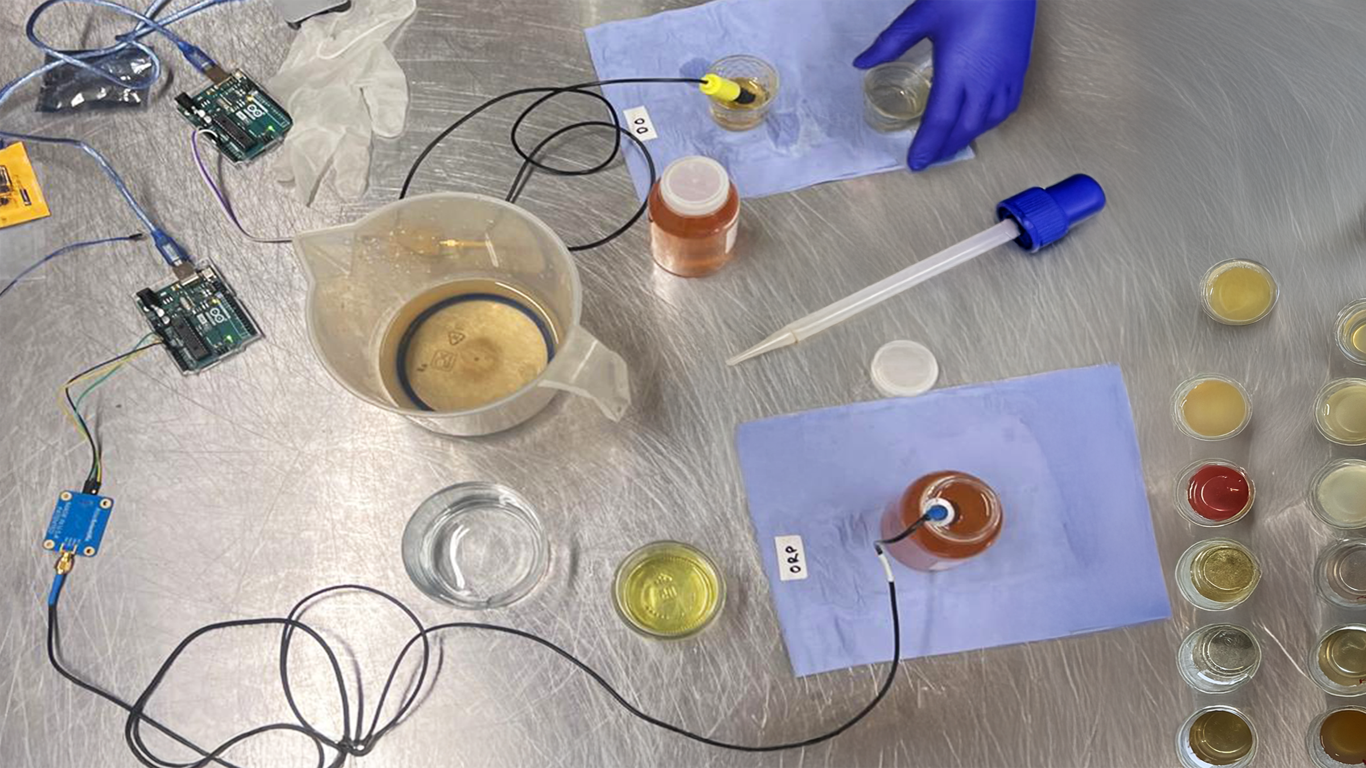
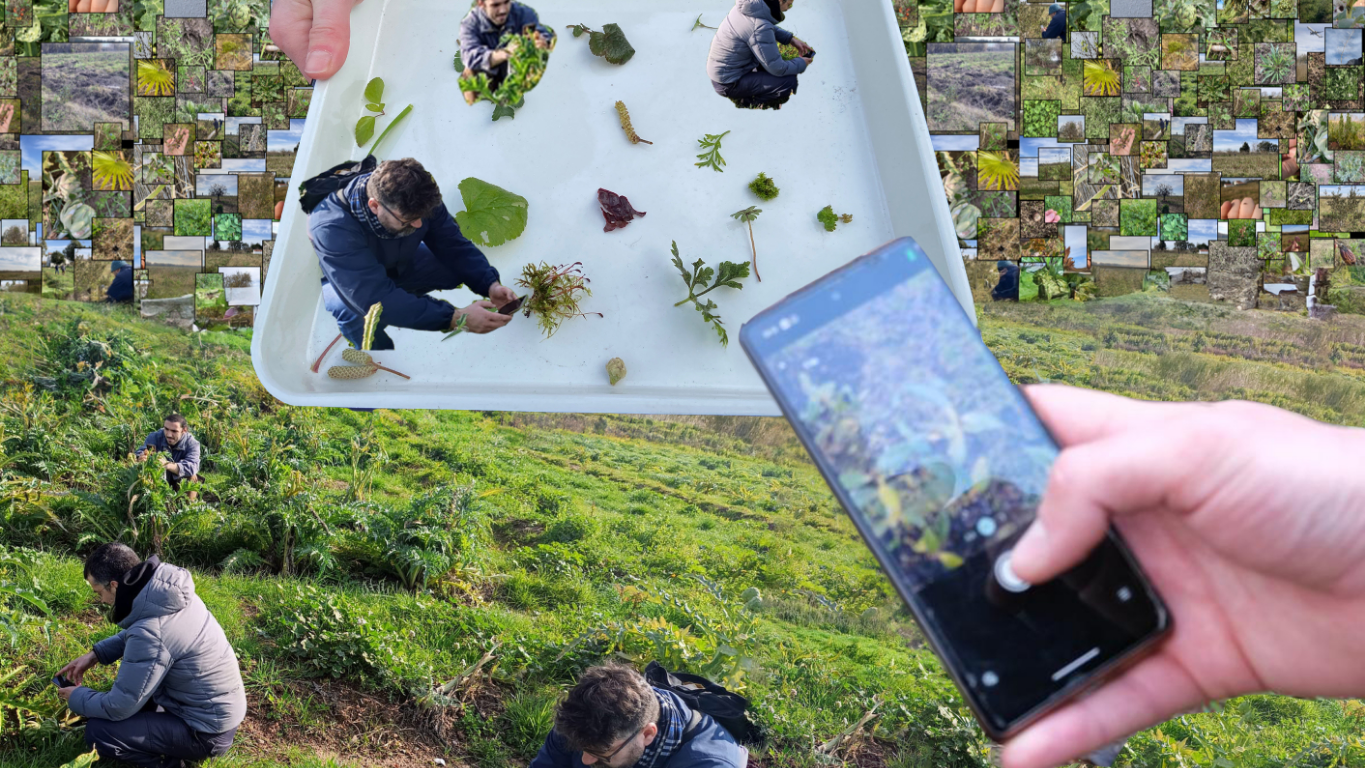
- Concepts and Prototypes, developed in the second art-tech residency, translate these scenarios into tangible prototypes and innovations with real-world applications.
FUTURE SCENARIOS
In the MUSAE project, future scenarios were developed by 12 artists during the first art-tech residency using the DFA method. These scenarios are grounded in rigorous research on emerging trends and developments in the Food as Medicine domain, combined with imaginative explorations of alternative futures. Future scenarios are designed to address key challenges and unlock new opportunities for technological innovation for companies. By leveraging these insights, companies can anticipate market shifts, inspire groundbreaking solutions, and drive innovation in the areas of Food as Medicine.
CONCEPTS AND PROTOTYPES
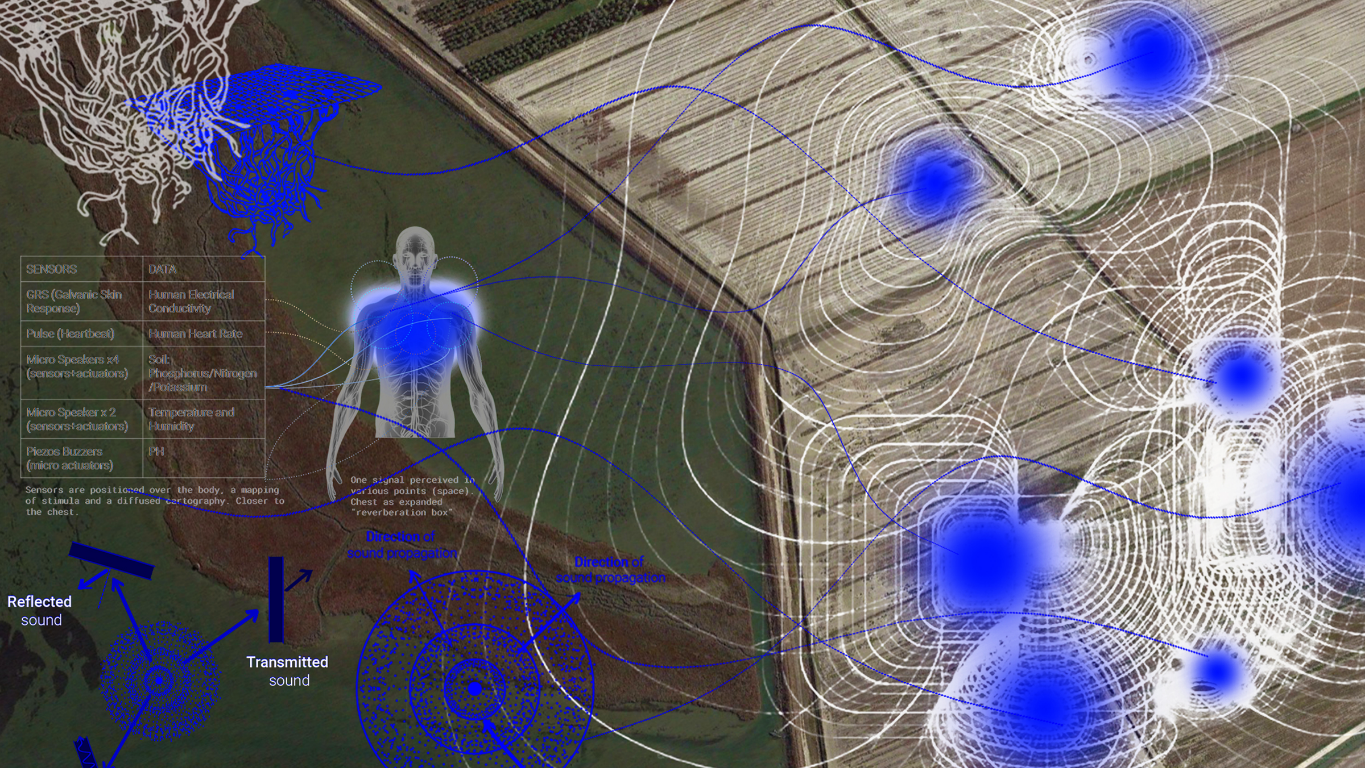
In the MUSAE project, concepts and prototypes were developed by 11 artists and 11 SMEs participating in the second MUSAE S+T+ARTS residency programme. Starting from the future scenarios, artist and SME collaboratively worked on the definition of a future-driven concept, which was later developed into TRL5 prototype. DFA method has guided teams in exploring the impact of the prototypes on environmental, societal and economic areas, as well as on their disruptive potnetial in specific sectors. These prototypes offer companies and Digital Innovation Hubs (DIHs) a valuable framework for advancing cutting-edge solutions, identifying new market opportunities, and driving sustainable innovation in the Food as Medicine domain.